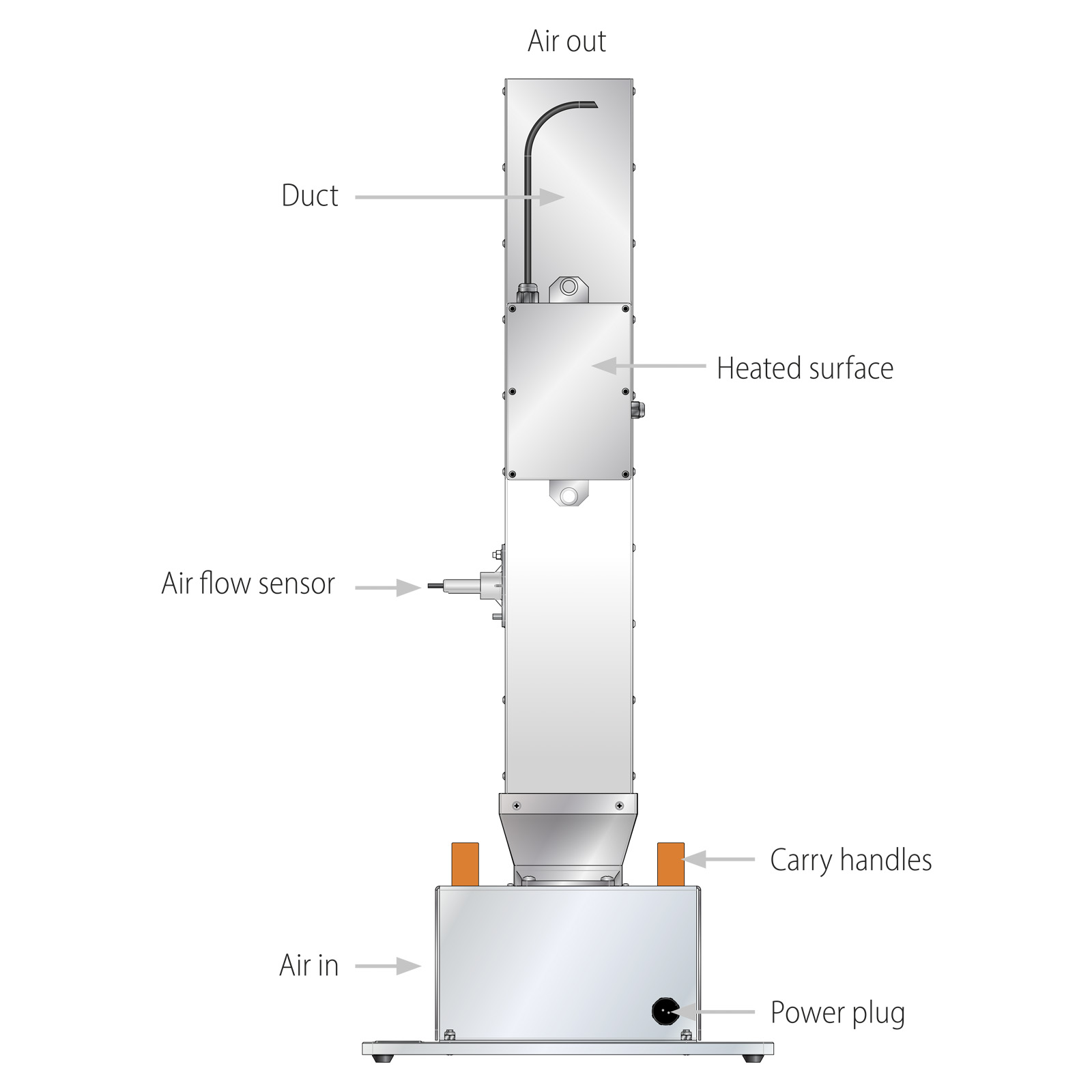
-
Products
-
Civil Engineering Testing Instruments
-
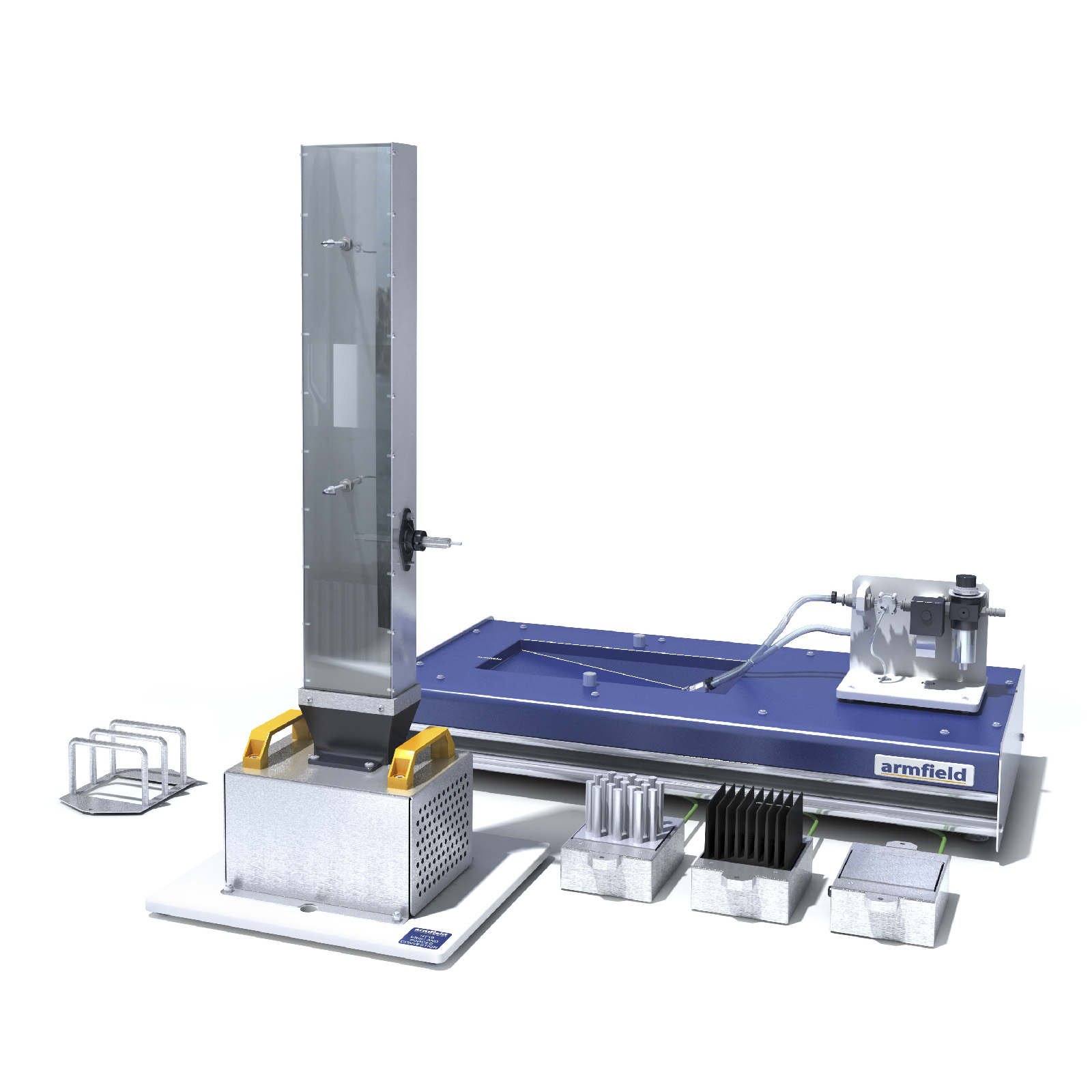
Material Testing Equipment
-
Transducer & Data loggerStrain Gauge
- General Use
- Waterproof
- High Temperature Use
- High and low temperature
- Cryogenic temperature use
- Weldable
- Concrete Material Use
- High Endurance
- For Plastic
- Wood, Gypsum Use
- For Magnetic Field
- Post-yield
- bending and tensile
- Stress Gauge
- Temperature
- Crack Detection
- Bolt Strain
- Sensor specific
- Strain Gage Related Products
- Load Cell
- Displacement
- Pressure
- Velocity/ Acceleration
- Stress
- Torque
- Temperature
- Tilt
- Water Content
- Pore Water Pressure
- Inertial Measurement Unit
- Static Strain Gauge Data Logger
- Dynamic Strain Transducer Data Logger
- Static Strainmeter
- Dynamic Strainmeter
- Portable Strainmeter
- Slope Movement Monitoring
- Strain Indicator
- Strain Gauge Calibration
- Frictional Type Torque Sensor
- Slip-ring type Wheel Torque Measurement
- Slip-ring type Wheel Force Transducer
- Vehicle Examination Transducer
-
Teaching and Research Laboratory EquipmentFluid Mechanics Advanced Fluid Mechanics Fluid Machine Thermodynamics Heat Transfer Renewable Energy Refrigeration & Air Conditioning Chemical Engineering Unit Operations Biochemical Engineering Water Treatment Applied Hydraulics & Hydrology Educational Food Technology Irrigation Water Management Internal Combustion Engine Process Control Teaching System Statics & Vibrations Fluid Science Engineering Fundamentals Machine Elements Naval Architecture
-
Digital Platform
-
Industrial Testing
-
Environmental Testing
-
Mobile impact crusher
-
Device Diagnostic Tool
-
-
Industry
-
Roads, Bridges, Airports, and Railways Engineering
-
Building and Infrastructure
-
- Solution
- Service
- News
- Community
- About
-
Products
-
Civil Engineering Testing Instruments
-
Material Testing Equipment
-
Transducer & Data loggerStrain Gauge
- General Use
- Waterproof
- High Temperature Use
- High and low temperature
- Cryogenic temperature use
- Weldable
- Concrete Material Use
- High Endurance
- For Plastic
- Wood, Gypsum Use
- For Magnetic Field
- Post-yield
- bending and tensile
- Stress Gauge
- Temperature
- Crack Detection
- Bolt Strain
- Sensor specific
- Strain Gage Related Products
- Load Cell
- Displacement
- Pressure
- Velocity/ Acceleration
- Stress
- Torque
- Temperature
- Tilt
- Water Content
- Pore Water Pressure
- Inertial Measurement Unit
- Static Strain Gauge Data Logger
- Dynamic Strain Transducer Data Logger
- Static Strainmeter
- Dynamic Strainmeter
- Portable Strainmeter
- Slope Movement Monitoring
- Strain Indicator
- Strain Gauge Calibration
- Frictional Type Torque Sensor
- Slip-ring type Wheel Torque Measurement
- Slip-ring type Wheel Force Transducer
- Vehicle Examination Transducer
-
Teaching and Research Laboratory EquipmentFluid Mechanics Advanced Fluid Mechanics Fluid Machine Thermodynamics Heat Transfer Renewable Energy Refrigeration & Air Conditioning Chemical Engineering Unit Operations Biochemical Engineering Water Treatment Applied Hydraulics & Hydrology Educational Food Technology Irrigation Water Management Internal Combustion Engine Process Control Teaching System Statics & Vibrations Fluid Science Engineering Fundamentals Machine Elements Naval Architecture
-
Digital Platform
-
Industrial Testing
-
Environmental Testing
-
Mobile impact crusher
-
Device Diagnostic Tool
-
-
Industry
-
Roads, Bridges, Airports, and Railways Engineering
-
Building and Infrastructure
-
-
-
-
-
- Solution
- Service
- News
- Community
- About
- 購買
- 中文
 Enquiry:hkmarketing@epc.com.hk
Enquiry:hkmarketing@epc.com.hk  Whatsapp Enquiry: +85261990717
Whatsapp Enquiry: +85261990717